Passage 1
Come on--Everybody′s doing it. That whispered message, half invitation and half forcing, iswhat most of us think of when we hear the words peer pressure. It usually leads to no good--drinking, drugs and casual sex. But in her new book Join the Club, Tina Rosenbe~ contends thatpeer pressure can also be a positive force through what she calls the social cure, in whichorganizations and officials use the power of group dynamics to help individuals improve their livesand possibly the word.
Rosenberg, the recipient of a Pulitzer Prize, offers a host of examples of the social cure inaction: In South Carolina, a state-sponsored antismoking program called Rage Against the Haze setsout to make cigarettes uncool. In South Africa, an HIV-prevention initiative known as loveLiferecruits young people to promote safe sex among their peers.
The idea seems promising, and Rosenberg is a perceptive observer. Her critique of the lamenessof many pubic-health campaigns is spot-on: they fail to mobilize peer pressure for healthy habits,and they demonstrate a seriously flawed understanding of psychology. "Dare to be different, pleasedon′t smoke!" pleads one billboard campaign aimed at reducing smoking among teenagers--teenagers, who desire nothing more than fitting in. Rosenberg argues convincingly that public-healthadvocates ought to take a page from advertisers, so skilled at applying peer pressure.
But on the general effectiveness of the social cure, Rosenberg is less persuasive. Join the Clubis filled with too much irrelevant detail and not enough exploration of the social and biologicalfactors that make peer pressure so powerful. The most glaring flaw of the social cure as it′spresented here is that it doesn′t work very well for very long. Rage Against the Haze failed oncestate funding was cut. Evidence that the loveLife program produces lasting changes is limited andmixed.
There′ s no doubt that our peer groups exert enormous influence on our behavior. An emergingbody of research shows that positive health habits--as well as negative ones--spread throughnetworks of friends via social communication. This is a subtle form of peer pressure: weunconsciously imitate the behavior we see every day.
Far less certain, however, is how successfully experts and bureaucrats can select our peergroups and steer their activities in virtuous directions. It′s like the teacher who breaks up thetroublemakers in the back row by pairing them with better-behaved classmates. The tactic neverreally works. And that′s the problem with a social cure engineered from the outside: in the realworld, as in school, we insist on choosing our own friends.
In the author′ s view, Rosenberg′ s book fails to __________.
- A.adequately probe social and biological factors
- B.effectively evade the flaws of the social cure
- C.illustrate the functions of state funding
- D.produce a long-lasting social effect
正确答案及解析
正确答案
解析
推断题。题于“在作者看来,Rosenberg的书未能_________”,本题是要问在作者眼中这本书的缺点.因此定位到文章第四段。第二句“Join the Club is filled with too much irrelevant detail and not enoughexploration of the social and biological factors that make peer pressure so powerful.”(书中充斥着太多无关的细节,却没有充分探索那些使同侪压力如此强大的社会和生物因素),只有A项“(未能)充分探究社会和生物因素”信息与之吻合.fails to adequately probe social and biological factors就是对原文not enough exploration of the socialand biological factors的同义再现。B项“(未能)有效避免社会治疗的缺点”原文未提,C项“(未能)阐释政府资助的功能”和D项“(未能)产生持久的社会效果”属于张冠李戴。
包含此试题的试卷
你可能感兴趣的试题
根据下列材料,按要求完成教学设计任务。
材料一:
《普通高中历史课程标准(2017 年版)》规定:通过了解三国两晋南北朝政权更迭的历史脉络,隋唐时期封建社会的高度繁荣,认识三国两晋南北朝至隋唐时期的制度变化与创新,民族交融、区域开发和思想文化领域的新成就。
材料二:
课文摘录:
唐朝是中国文学发展的又一个高峰。诗歌创作进入黄金时代。流传下来的有 2000 多位诗人创作的近 5 万首诗歌,很多脍炙人口的佳作,成为千古绝唱。李白、杜甫的诗作代表了唐诗的最高水平,他们分别被誉为“诗仙”和“诗圣”。
这一时期,书法、绘画、雕塑、舞蹈等大放光彩。书法在东汉末年成为一种艺术。魏晋南北朝时期,隶书、草书、楷书和行书等各种书体均已完备。东晋大书法家王羲之博采众长,诸体兼精,世称“书圣”。隋唐时期的书法艺术,融汇了南朝的秀美和北朝的雄健,创出新风格。颜真卿气势雄浑的颜体和柳公权骨力遒劲的柳体最为有名。魏晋南北朝的绘画,成就斐然。东晋开始出现知名的专职画家,以顾恺之为代表。他提出“以形写神”,所画人物栩栩如生,《女史箴图》和《洛神赋图》是他的代表作。隋唐的画坛,题材广泛,风格多样。宗教画生活气息浓厚,人物画注重表现人的形态,山水、花鸟也成为绘画主题。唐朝的吴道子被尊为“画圣”。魏晋至隋唐时期,因佛教广泛传播而修造的石窟寺很多。山西大同的云冈石窟、河南洛阳的龙门石窟、甘肃敦煌莫高窟等,都是闻名世界的艺术宝库

要求:根据课程标准要求和课文内容,设计出相关的教学过程,包括教学环节、教师活动和学生活动,并说明设计意图。
- 查看答案
怎么办呢,去罗马!那可是传说中的“上帝之城”,教皇的所在地,最接近上帝的地方。路德满怀期待地启程又满怀失望地回来了。为什么呢?因为路德发现自己被骗了:这哪里上帝之城?罗马灯红酒绿,神职人员不学无术、声色犬马。把灵魂交给这样的群体,怎么可能进天堂?路德想,看来得救还是得靠自己。从罗马回来后,路德专注于对于原始经典《圣经》的研究,获得了神学博士的学位。这一时期,他开始摆脱罗马教会的权威理论,对得救的方法和途径形成了自己的独立见解。
问题:
(1)对这位教师的讲述,你如何评价?请说出你的理由。(6 分)
(2)历史教师在讲授有关思想史的内容时应注意哪些问题?(10 分)
- 查看答案
材料一:
下面是某校历史学业水平考试中的一道试题。

材料二:
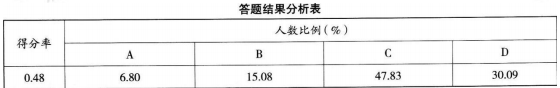
问题:
(1)这道题主要考查了什么内容和能力,难易度如何?(6 分)
(2)请从学生知识和题目命制两个方面,分析学生误选 D 项的原因。(6 分)
(3)针对上述原因,教师应采取哪些改进策略?(4 分)
- 查看答案
材料:
1905 年 8 月 9 日,在美国的调停下,日、俄在美国的朴茨茅斯开始谈判。9 月 5 日,日俄两国签订《朴茨茅斯和约》,重要条款包括:①俄国承认日本在朝鲜的独占利益;②俄国将辽东半岛的租借权、南满铁路及有关特权均无偿转让给日本;③以北纬 50 度为界,将库页岛南部及其附近岛屿让给日本;④俄国在中国东北撤兵,除辽东半岛外,东北的一切地方均交还中国。
——摘自齐世荣主编《世界史》现代卷
问题:
(1)材料中所说的《朴茨茅斯和约》签订的历史背景是什么?(8 分)
(2)根据材料并结合所学知识,概述这一和约对中国造成的危害。(8 分)
- 查看答案
简述高中与初中历史教学衔接应注意的问题。
- 查看答案