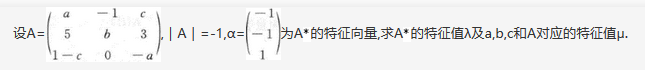
Text 1 Last year nearly one miUion Americans filed for bankruptcy.That is far fewer than the number who used to seek bankruptcy protection before the law was made tougher a decade ago.This reform may have done more harm than good.The aim of bankniptcy law is to give people relief from unpay-able debts.Some two-thirds of individual bankruptcies are due to a lost job.Many bankrupts need time to get back on their feet.In the mid-2000s Chapter 7 rules made it easy to wash away debts.That initated credit-card finns,which claimed that spendthrifts abused the system;so in 2005 the law was toughened.The idea was to shift people to a Chapter 13 bankruptcy,where they would have to repay some of the debt.The reform had a big impact.At least at first,Chapter 13 filings rose relative to Chapter 7 ones.And a new paper,from Stefania Albanesi,of the New York Federal Reserve,and Jaromir Nosal,of Columbia University,finds that the reform led to a permanent drop in the bankruptcy rate.However,other recent research suggests that this is not necessarily a good thing.Will Dobbie,of Princeton University,and Jae Song,of the SociaJ Securiiy AdminisLration,look at Chapter 13 bankrupLcies before the reforms of 2005.They link half a million bankruptcy filings to tax records and use a novel technique to analyse them.Because some bankruptcy judges are more merciful than others,people in similar straits may end up wiLh different bankruptcy decisions.This quirk allows some useful comparisons.Messrs Dobbie and Song argue that easier bankruptcy laws have good microeconomic effects.lf a creditor may no longer claim large chunks of a bankrupt's salary,that may increase his incentive to work-and decrease his need to slip out of town,change his job and close down his bank account.On average,those granted bankrupLcy eamed over 6,000 more in the subsequent year than similarly-placed plaintiffs who were rejected.The unlucky ones found it trickier to service their mortgages.Michelle White of the University of California,San Diego and colleagues found that bankruptcy reform caused the default rate on prime mortgages to rise 23%.Making consumer-bankruptcy law more debtor-friendly could hit Americans in other ways.If lenders are exposed to bigger losses,some argue,interest rates for such things as creditcards are bound to rise.But that danger can be overstated.Credit-card comparues may be reluctant to charge rates higher than their competitors'lest they attract more customers-those not put off by high rates because they know that,with luck,they won't have to pay their debts back.
Creditors are unlikely to raise their rates because_____
- A.they are restricted by the law
- B.consumers can't afford the debts
- C.they are stuck in fierce competition
- D.customers will not pay their debts back
正确答案及解析
正确答案
解析
细节题。根据按顺序定位原则,本题最有可能来自最后一段。其中creditors“债权人”=credit-card companies“信用卡公司”;are unlikely to“不太可能”=may be reluctant to“不愿意”;raise their rates“提高利率”-charge rates higher“收取更高利率”。故本题答案句为:lest they(competitors)attract more customers“以防竞争对手吸引更多顾客”。与该句同义替换的选项为[C]they are stuck in fierce competition“他们陷入激烈的竞争中”。选项[A]they are restricted bv the law“他们受到法律限制”:该项与答案句无关,故排除。选项[B]consumers can't afTord the debts“消费者无法负担这些债务”;该项can't afford一词属于无中生有。[D]customers will not pay their debts back“客户不会偿还债务”;该项与最后一句they won.t have lo pay their debts back相关,但与答案句无关,故也非正确答案。综上,本题选择[C]。